%20(1).png)
Our Services
At SP Scans, we offer a comprehensive range of advanced diagnostic imaging services designed to provide accurate and timely results. From MRI and CT scans to X-rays and ultrasounds, our state-of-the-art technology and experienced team ensure precise diagnoses to support your health journey. Explore our services and discover how we make quality care accessible and reliable for all.

MRI Scan
What is an MRI Scan?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan is a safe, non-invasive test that creates detailed images of your body, especially soft tissues like your brain, muscles, and organs.
How does it work?
The MRI machine uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed pictures of your body’s internal structures.
Why is it used?
An MRI helps doctors see inside your body without surgery. It’s used to:
-
Check for brain or spinal cord problems (like strokes, tumors, or injuries).
-
Look at joint and muscle issues (like torn ligaments, arthritis, or injuries).
-
Find signs of heart conditions or blood flow problems.
-
Detect cancer or monitor its progress.
-
Examine abdominal organs like the liver, kidneys, and uterus.
Preparation:
-
You may need to remove any metal objects (like jewelry or glasses).
-
Be empty stomach (for abdomen and MRCP).
CT Scan
What is an CT Scan?
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is an advanced imaging test that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of your body. It helps doctors see bones, organs, and tissues in great detail.
How does it work?
The CT scanner takes multiple X-ray images from different angles, which are then combined by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of your body.
Why is it used?
A CT scan is used to:
-
Check for injuries or trauma: It helps assess broken bones, internal bleeding, or damage from accidents.
-
Detect infections or inflammation: It can find abscesses, infections, or conditions like appendicitis.
-
Look for cancer: Helps detect tumors or monitor cancer progression.
-
Evaluate blood vessels: It can identify blockages or aneurysms in blood vessels.
-
Examine organs: Provides detailed images of the brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and more.
Preparation:
-
Be empty stomach.
-
Wear cotton dress.

Available Obstetric Ultrasound Scans:
-
Fetal viability scan.
-
NT scan (11 -14 weeks).
-
Obstetric scan routine.
-
Anamoly scan.
-
Fetal echo.
-
4D scan.
-
Fetal Biophysical score scan (32-36 weeks).
-
Obstetric Doppler Scan.
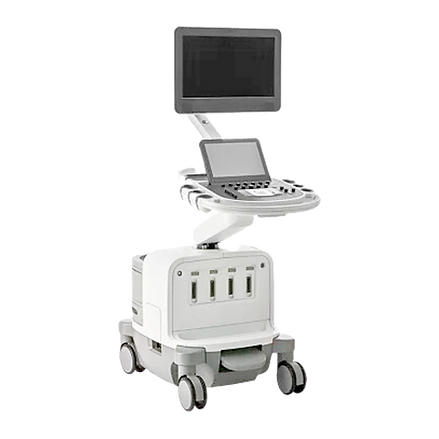
Ultrasound Scan
What is an Ultrasound Scan?
An ultrasound is a safe, non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the inside of your body, particularly soft tissues and organs.
How does it work?
During the ultrasound, a gel is applied to the area being examined. A small device called a transducer is moved over the area, sending and receiving sound waves to create images on a monitor.
Why is it used?
Ultrasound is commonly used to:
-
Monitor pregnancy: It helps track the baby’s development and check for any issues.
-
Examine organs: It can check the liver, kidneys, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen for conditions like cysts, tumors, or inflammation.
-
Evaluate the heart: Used to check for heart conditions and blood flow (known as an echocardiogram).
-
Diagnose musculoskeletal issues: Can assess muscles, tendons, and joints for injuries or inflammation.
-
Detect fluid buildup: Helps find fluid in areas like the abdomen or joints.
Preparation:
-
Drink water before the scan (for better imaging).
-
Wear loose clothing. Remove jewelry from the area being scanned.
X-Ray Scan
What is an X-Ray Scan?
n X-ray is a quick and commonly used imaging test that uses a small amount of radiation to create pictures of the inside of your body, particularly bones and certain organs.
How does it work?
During an X-ray scan, the body is exposed to a small amount of radiation. X-ray beams pass through the body and are absorbed by different tissues in varying amounts. A detector on the other side captures the image, which is then displayed on a monitor.
Why is it used?
An X-ray is typically used to:
-
Check for broken bones: Detect fractures, dislocations, and joint injuries.
-
Diagnose lung conditions: Such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung infections, or fluid in the lungs.
-
Detect infections or tumors: Helps identify conditions like tumors, infections, or other abnormalities in the chest, abdomen, or bones.
-
Evaluate bone and joint conditions: It helps to diagnose arthritis, degenerative conditions, or bone deformities




.png)
